Methods
children
children(self, at_level: int = -1) -> List['QuadKey']
Get all children of the specified level.
at_level(default: 1): Level of the children keys to be returned. Has to be less than the current QuadKey's level.
Example:
from pyquadkey2.quadkey import QuadKey
qk = QuadKey('0')
qk.children(at_level=2) # -> ['000', '001', '002', '003', '010', '011', '012', '013', '020', '021', '022', '023', '030', '031', '032', '033']
parent
parent(self) -> 'QuadKey'
Get the immediate parent QuadKey.
nearby
nearby(self, n: int = 1) -> List[str]
Get all QuadKeys at the same level that are in the current key's neighborhood of the specified radius n.
n(default: 1): Rectangular "radius" to consider.
Example:
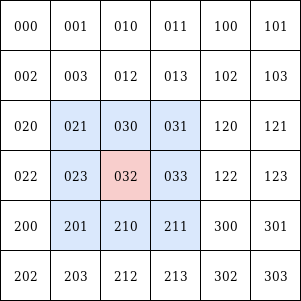
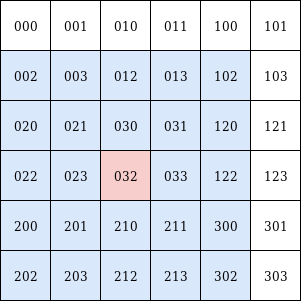
Left: n=1, right: n=2
from pyquadkey2.quadkey import QuadKey
qk = QuadKey('032')
qk.nearby() # -> ['021', '031', '023', '033', '201', '032', '030', '211', '210']
qk.nearby(n=2) # -> ['023', '012', '022', '212', '210', '021', '033', '300', '203', '200', '030', '102', '003', '031', '302', '201', '032', '202', '120', '213', '002', '013', '122', '211', '020']
is_ancestor
is_ancestor(self, node: 'QuadKey')
Whether or not the given key is an ancestor of the current one.
node: The other QuadKey to check against
is_descendent
is_descendent(self, node: 'QuadKey')
Whether or not the given key is a descendent of the current one.
node: The other QuadKey to check against
side
side(self)
Side length in meters of the current key's square projected onto a two-dimensional world map.
area
area(self)
Area in m² of the current key's square projected onto a two-dimensional world map.
difference
difference(self, to: 'QuadKey') -> List['QuadKey']
Returns all keys of the same level that are "between" (in two-dimensional space) the current key and a given one.
to: The second QuadKey
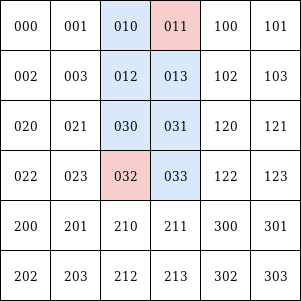
from pyquadkey2.quadkey import QuadKey
qk1 = QuadKey('032')
qk2 = QuadKey('011')
qk1.difference(qk1) # -> [011, 013, 031, 033, 010, 012, 030, 032]
to_tile
to_tile(self) -> Tuple[Tuple[int, int], int]
Returns the current key as a tile-tuple and the corresponding level.
to_pixel
to_pixel(self, anchor: TileAnchor = TileAnchor.ANCHOR_NW) -> Tuple[int, int]
Returns the current key as a pixel in a two-dimensional matrix.
anchor(default:TileAnchor.ANCHOR_NW): "Corner" of the current QuadKey's square / tile to get the pixel value for. Choices are:ANCHOR_NW,ANCHOR_SW,ANCHOR_NE,ANCHOR_SE,ANCHOR_CENTER.
to_geo
to_geo(self, anchor: TileAnchor = TileAnchor.ANCHOR_NW) -> Tuple[float, float]
Returns the current key as GPS coordinates.
anchor(default:TileAnchor.ANCHOR_NW): "Corner" of the current QuadKey's square / tile to get the geo coordinate value for. Choices are:ANCHOR_NW,ANCHOR_SW,ANCHOR_NE,ANCHOR_SE,ANCHOR_CENTER.
to_quadint
to_quadint(self) -> int
Returns the current key as 64-bit integer for better space efficiency.
anchor(default:TileAnchor.ANCHOR_NW): "Corner" of the current QuadKey's square / tile to get the geo coordinate value for. Choices are:ANCHOR_NW,ANCHOR_SW,ANCHOR_NE,ANCHOR_SE,ANCHOR_CENTER.
QuadKey.bbox (static)
bbox(quadkeys: List['QuadKey']) -> List['QuadKey']
Similar to difference, but as a static method. In addition this method accepts multiple keys and returns all keys, that are contained in a bounding box spanned by the two outer-most quadkeys.
from pyquadkey2.quadkey import QuadKey
qks = [QuadKey('032'), QuadKey('011')]
QuadKey.bbox(qks) # -> [011, 013, 031, 033, 010, 012, 030, 032]
QuadKey.from_geo (static)
from_geo(geo: Tuple[float, float], level: int) -> 'QuadKey'
See instantiation.
QuadKey.from_str (static)
from_str(qk_str: str) -> 'QuadKey'
See instantiation.
QuadKey.from_int (static)
from_int(qk_int: int) -> 'QuadKey'
See instantiation.